Burlington Public Library’s teen advisory group, TICOS (Teens Inspiring Changes, Optimism, and Service) has been selected to participate in the Democracy in Dialogue project sponsored by the Smithsonian.
As the world’s largest museum, education, and research complex, the Smithsonian Institute is helping to engage young people by asking, ‘how has your community played a role in 250 years of the American experiment?’ through the Democracy in Dialogue virtual exchange project.
In 2026 the United States will celebrate its 250th birthday, and this project encourages students from all walks to life to engage in discovery, dialogue, and reflection by exploring the complexities in our nation’s history.
From the significant role that Burlington played with the Sauk and Meskwaki people to being the territorial capital and hosting the first Free Public Library West of the Mississippi, this area has a rich history for teens to explore.
The unique cultural storytelling component of this project will be carried out with our teen mural installation in the teen area of the library.
This will be the library’s first permanent mural and will feature greater Burlington’s story along with notable people from the area.
“I am so excited for this opportunity for our area teens,” said Becky Ruberg, the BPL Teen Specialist.
“What an awesome experience for them!”
As part of this grant the teens will meet weekly at the library and will meet virtually with their exchange cohort in Springfield, Illinois, several times throughout the summer.
“We are incredibly proud of our TICOS kids and Becky Ruberg, for being selected for this prestigious program,” said Library Director Brittany Jacobs. “Partnerships like this open doors for area students to world-class thinkers and doers and inspire curiosity on a magnificent scale. What a wonderfully creative and impactful way for us to participate in reflections on 250 years of US history.”
If you know of any children…



 Participants visit the Keek-Och Tribal Farm.
Participants visit the Keek-Och Tribal Farm.
 The Lutheran Indian Mission Boarding School, located in Gresham, Wisconsin.
The Lutheran Indian Mission Boarding School, located in Gresham, Wisconsin.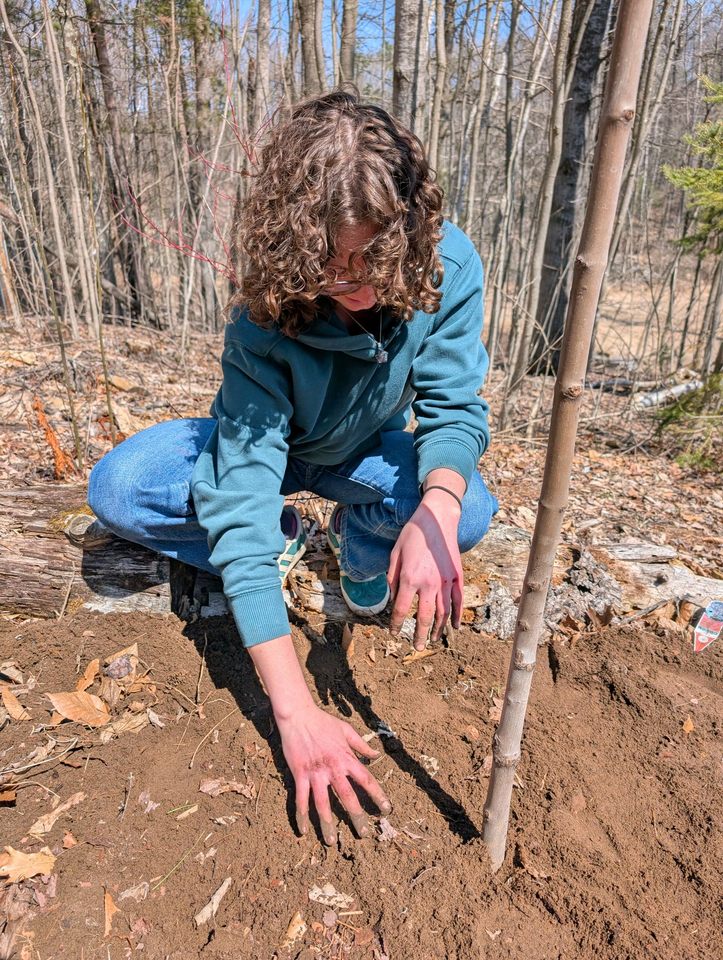
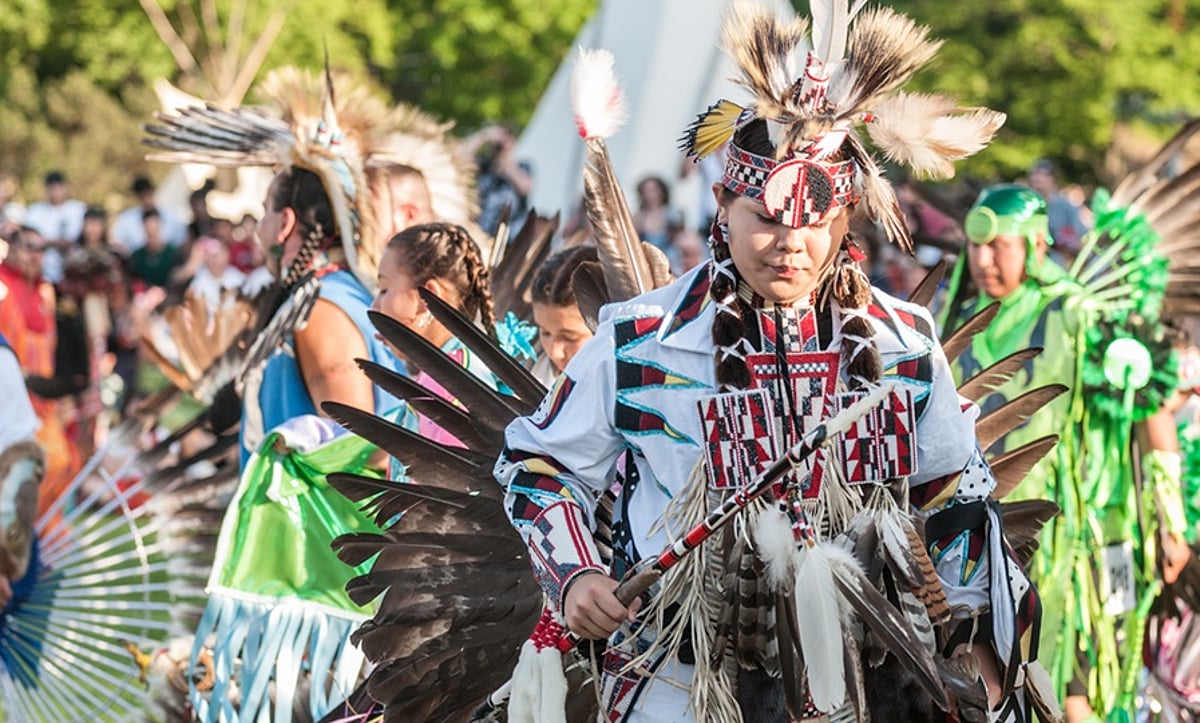







 Attendees of the 2024 Roanoke Island American Indian Festival Powwow in Manteo are shown here. Photo: Biff Jennings, courtesy Algonquian Indians of North Carolina, Inc.
Attendees of the 2024 Roanoke Island American Indian Festival Powwow in Manteo are shown here. Photo: Biff Jennings, courtesy Algonquian Indians of North Carolina, Inc. 
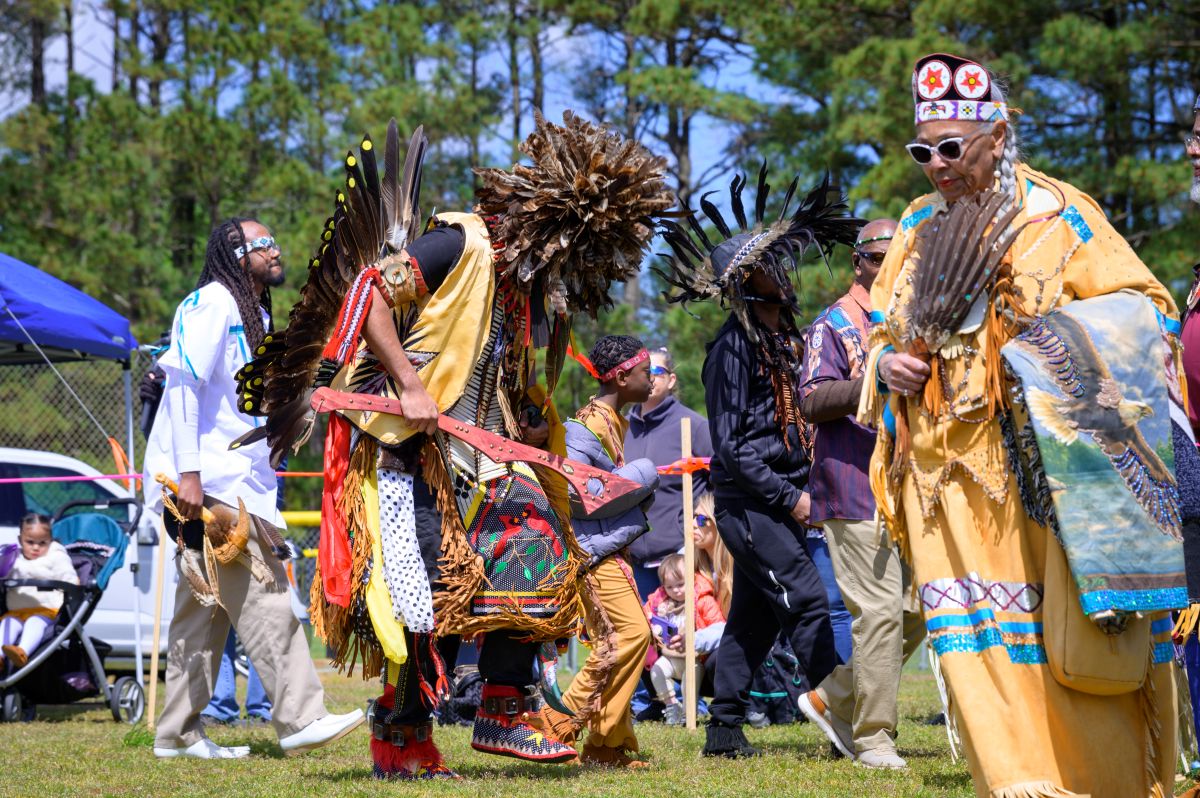
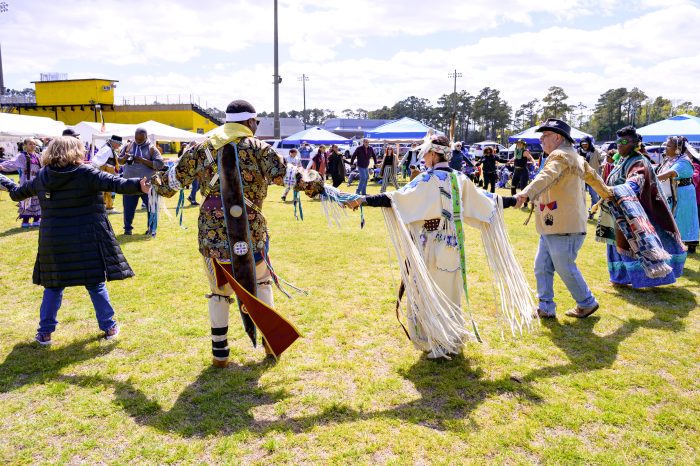 Dancing in the circle at the Roanoke Island Festival and Powwow at Manteo High School last year. Photo by Biff Jennings
Dancing in the circle at the Roanoke Island Festival and Powwow at Manteo High School last year. Photo by Biff Jennings  Single dancer at the Roanoke Island Festival and Powwow
Single dancer at the Roanoke Island Festival and Powwow